Treating Jumper’s Knee With Shockwave Therapy
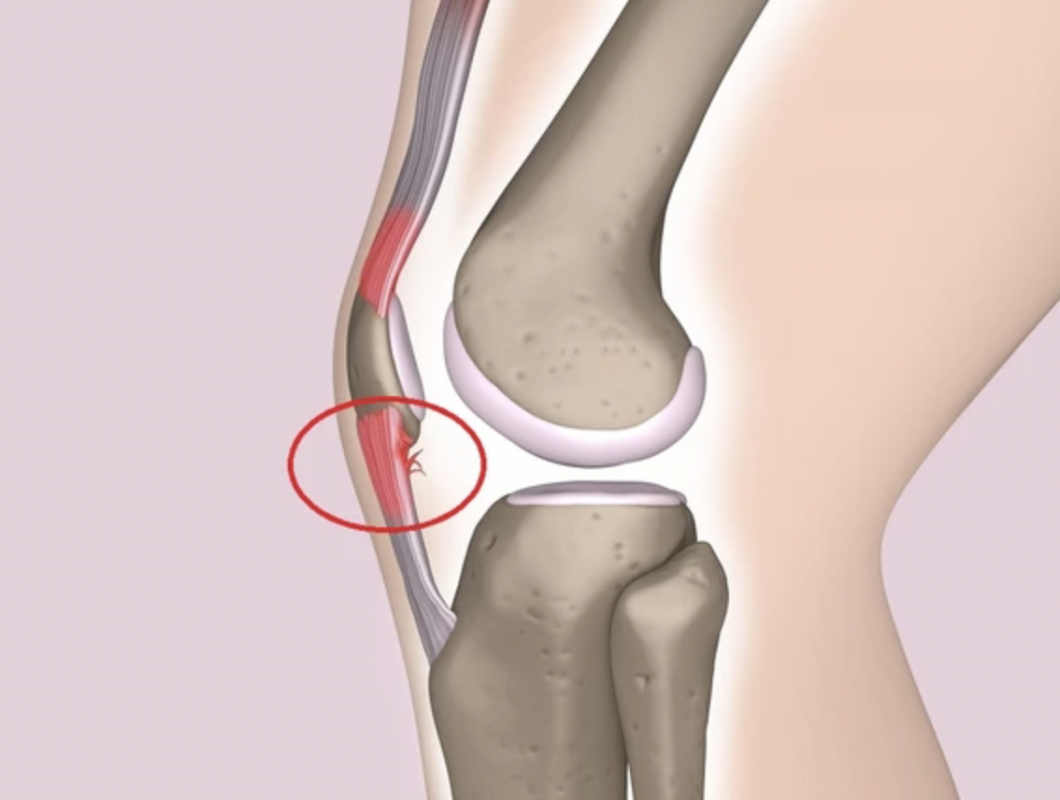
Patellar tendonitis, commonly known as Jumper’s Knee, is an injury to the patellar tendon, which connects the kneecap to the tibia and allows the quadriceps muscle in the thigh to pull the knee up, a movement extremely important for running, kicking, and jumping.
The injury is known as Jumper’s Knee due to its commonness in those who play sports involving a great deal of jumping, such as basketball, volleyball, soccer, and gymnastics. However, it’s also common in all types of physically active people.
The most common symptom of patellar tendonitis is pain behind the kneecap, and/or the point at which the tendon anchors to the tibia. Typically, this pain is most evident during periods of physical exertion. However, over time this pain will worsen to the point where it’s constant, and affects the ability to perform even everyday activities and movements.
Jumper’s Knee usually involves relatively minor swelling and microtearing of the patellar tendon. But if the issue isn’t addressed, the injury may become progressively worse, until the tendon finally tears completely.
Treating Jumper’s Knee with Shockwave Therapy
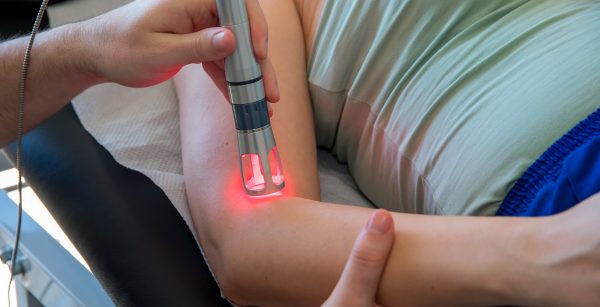
Patellar tendonitis involves damage to soft tissue through overuse and exertion. Because of the type of injury involved, Jumper’s Knee is a prime candidate for treatment with shockwave therapy (ESWT). ESWT is a non-invasive treatment which uses high-energy acoustic waves to stimulate injured soft tissues. This treatment encourages the growth of new nerves and blood vessels in targeted areas, and stimulates the body’s natural healing processes.
MYOSYTETM’s shockwave therapy treatment regimen is FDA-cleared and shown to be effective in treating Jumper’s Knee and other tendonitis-related ailments. Thanks to its non-invasive nature, shockwave therapy is often preferable to other modes of treatment, such as surgery or the use of potentially habit-forming painkillers.
While the reasons for shockwave therapy’s effectiveness are currently not comprehensively understood, several studies have demonstrated its effectiveness in eliminating tendonitis-related pain and its underlying causes.
Other forms of therapy, such as pulsed magnetic field therapy (PEMFT) and laser therapy may also be effective in treating Jumper’s Knee and related disorders.